Research Overview
Research in the Bing Xia Lab is focused on the roles of DNA damage, oxidative stress and autophagy in cancer development. Much of our research program originated from our discovery of the PALB2 tumor suppressor, which functionally links BRCA1 and BRCA2, the two major breast cancer suppressor proteins in the DNA damage response. The three proteins play essential roles in homologous recombination-based DNA double strand break repair and DNA damage-induced cell cycle checkpoint control, which are critical to the maintenance of genome integrity and suppression of cancer development. Inherited mutations in these genes greatly increase cancer risk, particularly in the breast, ovary, pancreas and prostate.
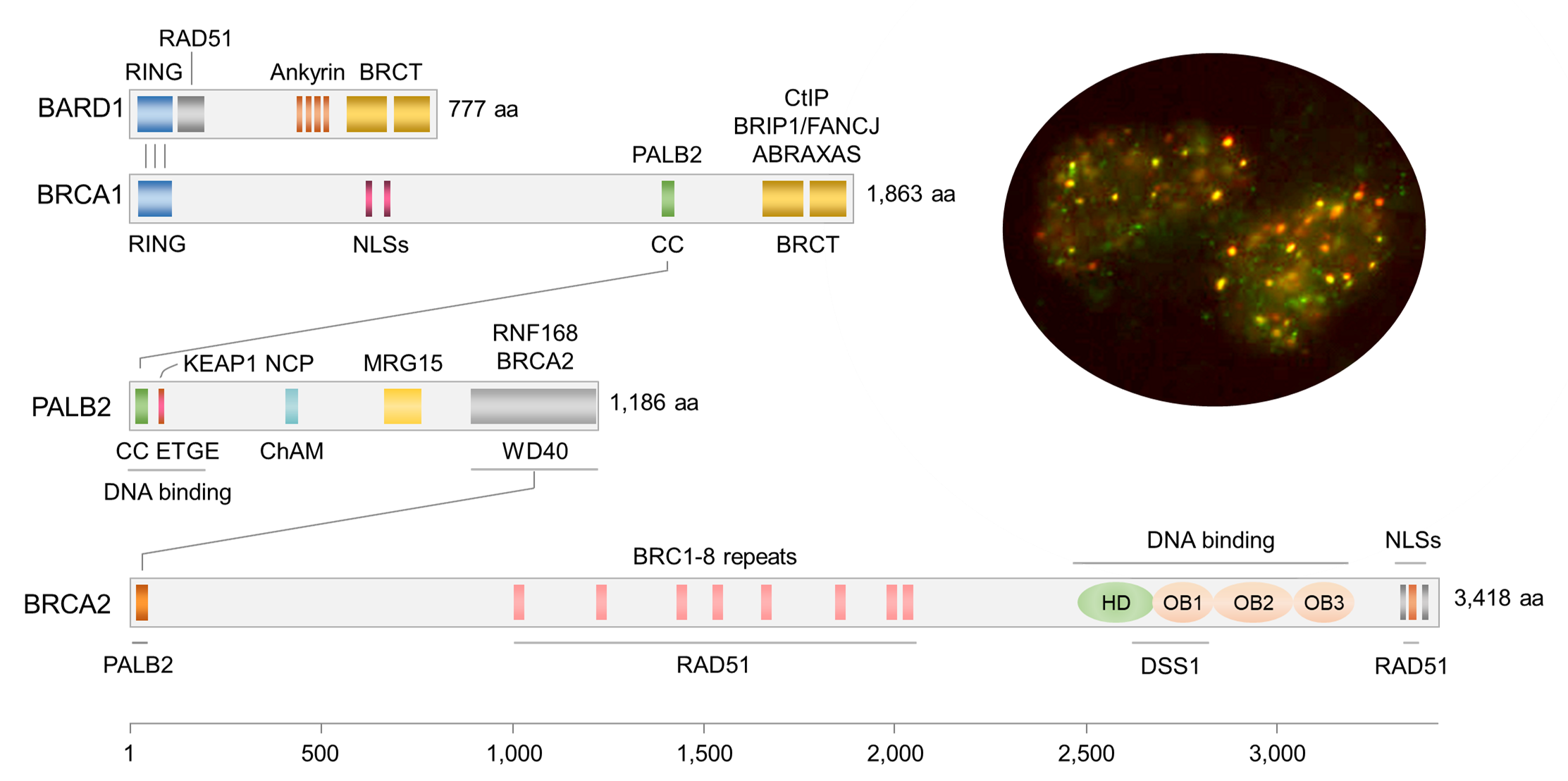
In addition to the DNA damage response, we found that PALB2 also participates in cellular redox regulation via a direct binding to KEAP1, a sensor of oxidative stress and a powerful negative regulator of NRF2, a master antioxidant transcriptional factor. Interestingly, BRCA1 has also been implicated in the regulation of NRF2-mediated antioxidant response, suggesting that oxidative stress may play a key role in tumor development following the loss of these tumor suppressors. Moreover, we have also found that autophagy, an intracellular waste disposal, nutrient recycling and oxidative stress mitigation mechanism, may be an important facilitator of PALB2-associated tumor development.
Currently, we are pursuing the following lines of study:
-
Mechanistic analyses of the BRCA1-PALB2-BRCA2 and KEAP1-NRF2 pathways in the DNA damage response and oxidative stress response;
-
Mouse models of BRCA- and PALB2-associated tumor development, focusing on the roles of DNA damage, oxidative stress and autophagy throughout the process; and
-
Functional characterization of clinically relevant BRCA1, BRCA2 and PALB2 mutations in DNA repair and therapy resistance.
Through these studies, we aim to shed light on the molecular mechanisms and developmental path of BRCA/PALB2-associated cancers, and contribute to the prevention and treatment of the diseases.


